Ternary Operator Javascript - Write Cleaner Code
In this tutorial, you will know about the ternary operator in JavaScript, how to use it and how to write cleaner code using it 👨💻.
Ternary Operator in JavaScript
The ternary operator is a shorthand for an if-else statement. It is a concise way to check a condition and return a value based on it.
The ternary operator is the only javascript operator which takes 3 operands for the operations.
The basic syntax of the ternary operator is as follows:
condition ? valueIfTrue : valueIfFalse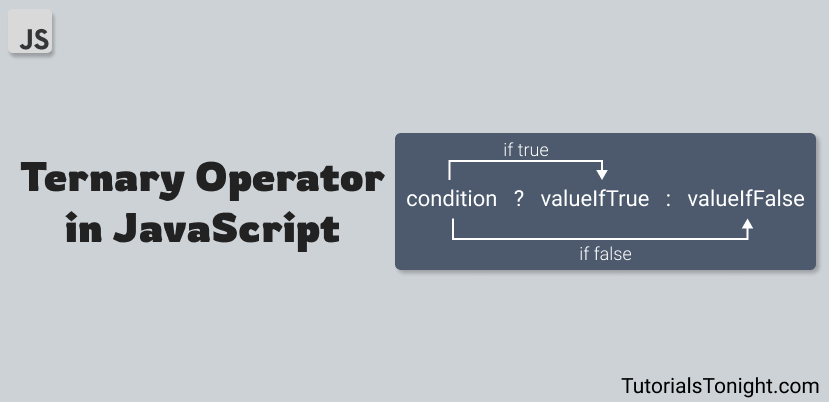
Here is the most basic example of a ternary operator. Where we are just using it to print a message.
Example
// condition ? expression1 : expression2
true ? alert("Condition is true") : alert("condition is false");
// evaluating condition => (10 > 5) returns true
10 > 5 ? console.log("Yes 10 > 0") : console.log("No!");Let's see another example that checks if a person is older than 18 years or not and returns a message accordingly.
Example
let age = 25;
let canDrink = (age > 18) ? 'Yes' : 'No';
console.log(canDrink); // Output: 'Yes'Another example, let's say we have a variable score and we want to check if the student passed or failed.
Example
let score = 50;
let result = (score > 40) ? 'Pass' : 'Fail';
console.log(result); // Output: 'Pass'Ternary operator VS if-else
The following table shows the differences between the ternary operator and the if-else statement.
| Ternary Operator | if-else Statement |
|---|---|
Syntax: condition ? valueIfTrue : valueIfFalse | Syntax: if (condition) { code to execute if true } else { code to execute if false } |
Short and concise way to write a simple if-else statement | More versatile, can be used for more complex conditions |
| Best for simple conditions and when you only need to return one value | Can be used for multiple conditions and can execute different code based on the outcome |
| Limited to only one condition | Can handle multiple conditions |
| Limited to only one value return | Can handle multiple return values |
The following example compares the ternary operator and if-else statement.
- Ternary operator
- If else
let mark = 50;
// using ternary
mark >= 40 ? console.log("Pass!") : console.log("Fail!");let mark = 50;
// using if else
if (mark >= 40) {
console.log("Pass!");
}
else {
console.log("Fail!");
}You can see that the ternary operator is much easier to read and understand than if-else.
Ternary operator without else
The name of the ternary operator itself claims that it takes 3 operands. In the ideal case, you need to provide all 3 operands to make it work.
But you can also work without the else part using different syntax.
condition && valueIfTrueLet's see an example of a ternary operator without else.
Example
let price = 10;
let discount = 3;
let discountedPrice = (discount > 0) && (price - discount);
console.log(discountedPrice); // Output: 7Ternary operator multiple conditions
The ternary operator can also be used to check multiple conditions and assign a value to a variable based on that.
Let's see an example of how to take multiple conditions with a ternary operator.
Example
const num = 15;
// is divisible by 3 and 5
const isDivisibleBy3And5 = (num % 3 === 0 && num % 5 === 0) ? true : false;
console.log(isDivisibleBy3And5);Here is another example of multiple conditions with the ternary operator.
Example
let age = 22;
// find age group
let group = age < 18 ? "underage" : age < 65 ? "adult" : "elder";
console.log(group);If you do not understand how it resulted in "adult" then here is a little more explanation.
The ternary operator is a combination of multiple conditions. The condition given (age < 18) is false in the above code so it jumped to the next condition (age < 65) and return true.
Look at the code below it is the ternary operator in multiple lines.
Same as the above code
let age = 22;
// find age group
let group = age < 18 ? "underage" // if
: age < 65 ? "adult" // else if
: "elder"; // else
console.log(group);Nested Ternary Operator javascript
Ternary operators can also be nested to check multiple conditions same as if-else but it becomes more complicated to read and also is not recommended.
First, look at the code to find leap year using if-else statements.
Example
const year = new Date().getFullYear();
let isLeapYear;
if (year % 4 === 0) {
if (year % 100 === 0) {
if (year % 400===0) {
isLeapYear = "a leap year";
}
else {
isLeapYear = "not a leap year";
}
}
else {
isLeapYear = "a leap year";
}
}
else {
isLeapYear = "not a leap year";
}
console.log(year + " is " + isLeapYear);Now let's see how to use the ternary operator to check if a year is a leap year.
Example
const year = new Date().getFullYear();
const isLeapYear = year % 4 === 0 ? (year % 100 === 0 ? (year % 400 === 0 ? "a leap year" : "not a leap year") : "a leap year") : "not a leap year";
console.log(year + " is " + isLeapYear);Ternary operator in loops
Ternary operators can also be used in loops. It is very useful when you want to check a condition in a loop.
Let's see an example of how to use the ternary operator in a loop.
Example
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = numbers.map(number => number > 3 ? "bigger than 3" : "smaller than 3");
console.log(result);Ternary operator Examples
Here are 10 different examples that use the ternary operator.
1. Checking for odd or even numbers:
Example
let num = 5;
let result = (num % 2 == 0) ? 'even' : 'odd';
console.log(result); // Output: 'odd'2. Assigning a value to a variable based on a condition:
Example
let age = 25;
let canVote = (age >= 18) ? true : false;
console.log(canVote); // Output: true3. Returning different values based on a condition:
Example
let score = 75;
let grade = (score >= 90) ? 'A+' : (score >= 80) ? 'A' : (score >= 70) ? 'B' : (score >= 60) ? 'C' : 'F';
console.log(grade); // Output: 'B'4. Setting a default value for a variable:
Example
let name = "";
let displayName = (name) ? name : "Guest";
console.log(displayName); // Output: 'Guest'5. Checking if a string is empty or not:
Example
let str = "Hello";
let checkString = (str == "") ? true : false;
console.log(checkString); // Output: false6. Choosing between two different actions based on a condition:
Example
let x = 10;
let action = (x > 5) ? function(){console.log("x is greater than 5")} : function(){console.log("x is less than or equal to 5")};
action(); // Output: "x is greater than 5"7. Setting a variable to a string or number based on a condition:
Example
let y = "Hello";
let z = (typeof y === 'string') ? "y is a string" : 100;
console.log(z); // Output: "y is a string"8. Displaying a message based on a condition:
Example
let isLoggedIn = true;
console.log(isLoggedIn ? "Welcome back!" : "Please log in to continue."); // Output: "Welcome back!"9. Assign a variable to the maximum of two values:
Example
let a = 5;
let b = 10;
let max = (a > b) ? a : b;
console.log(max); // Output: 1010. Check if a number is between two numbers:
Example
let num = 5;
let between = (num > 0 && num < 10) ? true : false;
console.log(between); // Output: trueFrequently ask questions
-
How do you use multiple conditions in a ternary operator?
You can separate multiple conditions with logical operators like
&&or||and use the ternary operator as it is. -
Can ternary operator have multiple statements?
Yes, you can have multiple statements inside the ternary operator.
For example:a ? b : c ? d : e. -
Can ternary operator have multiple lines?
Yes, you can have multiple lines inside the ternary operator.
For example:a ? b : c ? d : e
