Python Program to Find Lcm of Two Numbers
In this tutorial, we will learn how to find the LCM of two numbers in Python using 4 different methods.
LCM stands for Least Common Multiple. It is the smallest number that is divisible by both numbers.
For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest number that is divisible by both 2 and 3. Similarly, the LCM of 15 and 25 is 75.
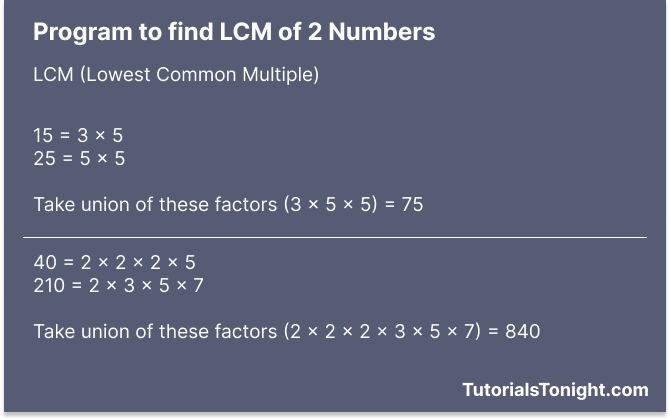
Mathematically, the LCM of two numbers is the product of the union of prime factors of both numbers. Look at the above image to understand this.
There is also a relationship between GCD (Great Common Divisor) and LCM. The LCM of two numbers is equal to the product of both the numbers divided by their GCD.
LCM(a, b) = (a * b) / GCD(a, b)
Now let's look at the python program to find the LCM of two numbers.
Method 1
The first approach to find LCM is to start checking from the maximum of the two numbers and incrementing it by the maximum of the two numbers until we find a number that is divisible by both numbers.
Note: You can increment by 1 each time or by the minimum of the two numbers as well but this will make the program slower and will reach the same result.
def lcm(a, b):
max = a if a > b else b
for i in range(max, a*b+1, max):
if (i%a == 0) and (i%b == 0):
lcm = i
break
return lcm
print(f"LCM of 2 and 3 is {lcm(2, 3)}")
print(f"LCM of 15 and 25 is {lcm(15, 25)}")Output:
LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 LCM of 15 and 25 is 75
Method 2 ⭐️⭐️
The second approach to find LCM is to find the prime factors of both numbers and then multiply them to get the LCM.
For this follow the steps given below:
- Start a Python for loop from 2 to half of the minimum of the two numbers.
- Check if the number is a factor of both numbers. If yes, then divide both the numbers by that number and multiply the number to the 'lcm' variable.
- Repeat the above steps until the number is not a factor of both the numbers.
- Finally, multiply the LCM with the remaining numbers.
def lcm(a, b):
# find the minimum of the two numbers
min = a if a < b else b
lcm = 1
for i in range(2, min//2+1):
# keep dividing the numbers by the number if it is a factor
# and multiply the number to the LCM
while a % i == 0 and b % i == 0:
a = a / i
b = b / i
lcm = lcm * i
lcm = int(lcm * a * b)
return lcm
print(f"LCM of 4 and 6 is {lcm(4, 6)}")
print(f"LCM of 4 and 6 is {lcm(98, 54)}")Output:
LCM of 4 and 6 is 12 LCM of 98 and 54 is 2646
Method 3 ⭐️⭐️⭐️
The third approach to find LCM is to use the fact that LCM(a, b) = (a * b) / GCD(a, b).
So, we can find the GCD of the two numbers and then divide the product of the two numbers by the GCD to get the LCM.
In python, we have a built-in function gcd() to find the GCD of two numbers.
from math import gcd
def lcm(a, b):
return (a * b) // gcd(a, b)
print(f"LCM of 4 and 6 is {lcm(4, 6)}")
print(f"LCM of 98 and 54 is {lcm(98, 54)}")Output:
LCM of 4 and 6 is 12 LCM of 98 and 54 is 2646
Performance Comparison
Let's compare the performance of all the above methods.
import timeit
def method1(a, b):
max = a if a > b else b
lcm = 1
for i in range(max, a*b+1, max):
if (i%a == 0) and (i%b == 0):
lcm = i
break
return lcm
def method2(a, b):
min = a if a < b else b
lcm = 1
for i in range(2, min//2+1):
while a % i == 0 and b % i == 0:
a = a / i
b = b / i
lcm = lcm * i
lcm = int(lcm * a * b)
return lcm
from math import gcd
def method3(a, b):
return (a * b) // gcd(a, b)
print("Method 1:", timeit.timeit("method1(98, 54)", setup="from __main__ import method1", number=100000))
print("Method 2:", timeit.timeit("method2(98, 54)", setup="from __main__ import method2", number=100000))
print("Method 3:", timeit.timeit("method3(98, 54)", setup="from __main__ import method3", number=100000))Output:

From the above result, you can see method 3 is the fastest method.
Conclusion
This is the end of the tutorial on how to find LCM of two numbers in python. The most efficient method to find the LCM is to find the GCD of the two numbers and then divide the product of the two numbers by the GCD to get the LCM.
