Javascript Number Properties And Methods
In this tutorial, you will learn how numbers are handled in JavaScript. You will learn about different mathematical operations on numbers, how to convert numbers to strings, how to round numbers, how to format numbers, and how to convert strings to numbers.
JavaScript Number
In javascript, the Number is a primitive data type. It represents all numerical values like:
- Integer - 2, 5, 18, 100, 55, etc
- Float - 1.0, 2.5, 8.4503, 245.50, etc
- Exponential - 1.23e5, 1.23e-5, etc
- Binary - 0b1010, 0b1111, etc
- Octal - 0o7, 0o77, 0o777, etc
- Hexadecimal - 0xFF, 0xFFF, 0xFFFF, etc
- etc
The numbers in javascript is always stored in double-precision floating-point numbers means it can store both integral and fractional values.
- Number can only keep precision of 17 digits.
- The largest number that can be stored in a double-precision floating-point number is 1.7976931348623157E+308 ≈ 1.8E+308
There are two ways to define numbers in javascript:
- Number literals - Like 10, 25, 45, etc
- Number Constructor - It can convert any string or other data type to a number. If it is not convertible to a number then it gets converted to
NaN.
Generally, browsers automatically convert Number literals to instances of Number class.
Example
// Number literals
const num1 = 15;
const num2 = 12.55;
console.log(num1, typeof num1);
console.log(num2, typeof num2);
// Number constructor
const num3 = Number(15);
const num4 = Number(12.55);
console.log(num3, typeof num3);
console.log(num4, typeof num4);Creating Javascript Number Using Constructor
To create a number using number constructor use Number() as function/constructor and pass the number as an argument. Example Number(20), Number(35.5), Number('12') etc.
Example
const num1 = Number(15);
const num2 = Number(12.55);
console.log(num1, typeof num1);
console.log(num2, typeof num2);
// Convert string to number
console.log('1250');Ways to write a number in Javascript
Generally, we write numbers in decimal format. But there are some ways to write numbers in javascript.
1. Decimal Method
The number system that we use in our daily life is the decimal number system. Numbers in the decimal number system ranges from 0-9. Defining numbers using a combination of 0-9 is a decimal number.
Example
const num1 = 50;
const num2 = 12.54;
console.log(num1, num2);2. Exponential Method
While writing numbers like 1 billion or 1 trillion in numbers we would have to write like 100000000 and 10000000000 respectively, which is very inconvenient.
Javascript provides a method to write such numbers in an easier manner. We can shorten the number by appending 'e' or 'E' to the number and then specifying the number of 0's after it. Example, 1000 can be written as 1e3, 0.002 as 2e-3, 50000 as 5e4 etc. This is the exponential method of writing numbers.
Example
const num1 = 23e2;
console.log(num1);
const num2 = 1e7;
console.log(num2);
const num3 = 123456e-3;
console.log(num3);
const num4 = 0.00234e10;
console.log(num4);
const num5 = 99545e-9;
console.log(num5);3. Other Number System
There exist other number systems apart from decimal number systems like binary, octal, hexadecimal, etc.
hexadecimal numbers are widely used in the hex color system.
The hexadecimal number is defined by the suffix 0x in the number. example 0xff, 0x25, etc.
Example
const num1 = 0xff;
const num2 = 0xFF; // case doent't matter -- 255
const num3 = Number(0x22);
const num4 = Number(0x1e2);
console.log(num1, num2, num3, num4);Binary numbers include only 2 different numbers, 0's and 1's. It is defined by adding the suffix 0b in the number. example 0b1010, 0x11 etc.
Example
const num1 = 0b1111;
const num2 = 0b1010;
const num3 = Number(0b1000001);
const num4 = Number(0b111110001);
console.log(num1, num2, num3, num4);Octal numbers includes 8 different digits in their numbers 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7. It is defined by adding the suffix 0o in the number. example 0o45, 0o22 etc.
Example
const num1 = 0o7;
const num2 = 0o45;
const num3 = Number(0o30);
const num4 = Number(0o255);
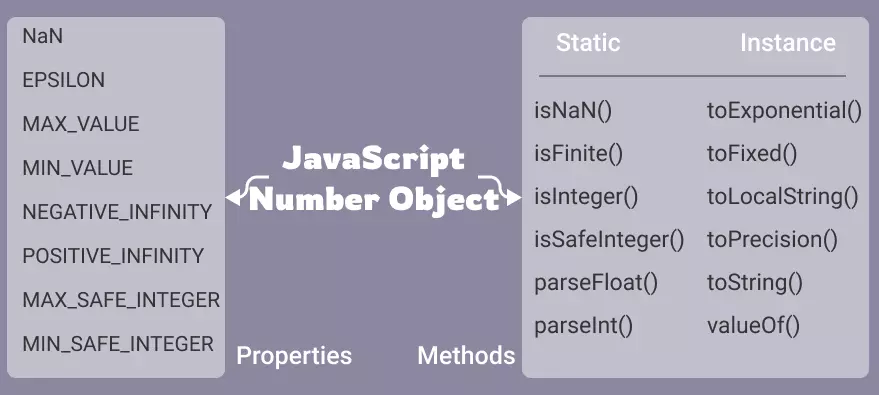
console.log(num1, num2, num3, num4);Javascript Number Properties
Number is a global object in javascript, it has many properties.
All the properties of Number are static like properties of math.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Number.EPSILON | The smallest interval between two numbers |
| Number.MAX_VALUE | The largest positive representable number |
| Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER | Maximum safe integer in javascript is 253 - 1 |
| Number.MIN_VALUE | The smallest positive representable number. The smallest number just greater than 0 |
| Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER | Minimum safe integer in javascript is -(253 - 1) |
| Number.NaN | Not a Number |
| Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY | Represent negative Infinity |
| Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY | Represent positive Infinity |
Example
console.log(Number.EPSILON);
console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE);
console.log(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);
console.log(Number.MIN_VALUE);
console.log(Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER);
console.log(Number.NaN);
console.log(Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY);
console.log(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY);Javascript Number methods
Number methods in javascript help us to work with numbers. A primitive value such as 2, 18, etc can't have properties and methods but when we call methods on these values javascript treats it as an object.
- isNaN()
- isFinite()
- isInteger()
- isSafeInteger()
- parseFloat()
- parseInt()
- toExponential()
- toFixed()
- toLocalString()
- toPrecision()
- toString()
- valueOf()
1. isNaN In Javascript
The isNaN() method is a global function that determines whether the given value is NaN (Not A Number) or not. If the passed value is NaN then it returns true else returns false.
You can alternatively also use Number.isNaN.
Why do we need the isNaN method?
Unlike other values in javascript, we can't compare a NaN value with another NaN. Since both NaN == NaN and NaN === NaN are false. Hence, we need the isNaN method to check whether a number is NaN or not.
Example
console.log(isNaN(NaN));
console.log(isNaN(10));
console.log(isNaN("abc"));
console.log(isNaN());2. isFinite In Javascript
The isFinite() method is a global function that determines whether the given value is a finite number or not. The passed value is also converted to a number if it is possible.
If the passed value is either NaN, positive infinity, or negative infinity then this method returns false else return true.
Example
console.log(isFinite(100));
console.log(isFinite(1000));
console.log(isFinite("abc"));
console.log(isFinite("20"));
console.log(isFinite(NaN));
console.log(isFinite(Infinity));
console.log(isFinite(-Infinity));3. isInteger In Javascript
The isInteger() method determines whether the given value is an integer or not.
If the passed value is either NaN, positive infinity or negative infinity then this method returns false and returns true for numbers.
Example
console.log(Number.isInteger(10));
console.log(Number.isInteger(Math.PI));
console.log(Number.isInteger(22.15));
console.log(Number.isInteger(-25));
console.log(Number.isInteger(true));
console.log(Number.isInteger(NaN));
console.log(Number.isInteger(Infinity));
console.log(Number.isInteger(-Infinity));4. isSafeInteger In Javascript
The isSafeInteger() method determines whether the given value is a safe integer or not.
A safe integer is a number that can be exactly represented as an IEEE-754 double-precision number ie. all integers from -(253 - 1) to (253 - 1).
The isSafeInteger() method returns true if the value is of type Number and is a safe integer.
Example
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(10));
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(Math.PI));
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(Math.pow(2, 53) - 1));
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(-(Math.pow(2, 53) - 1)));
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(Math.pow(2, 53)));
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(NaN));
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(Infinity));5. parseFloat In Javascript
The Number.parseFloat() or parseFloat() method parses an argument and returns a floating-point number. If the number can't be parsed then it returns NaN.
You can use it to take out numerial values from real life units like "55kg", "120px", "220km", etc.
If the first character can not be converted to a number then it returns NaN.
Example
console.log(parseFloat("55kg"));
console.log(parseFloat("125.55px"));
console.log(parseFloat("abc"));6. parseInt In Javascript
The Number.parseInt() or parseInt() method is same as parseFloat method but it only extracts integer value from the passed value.
parseInt also accepts an optional argument which is radix (the base in a mathematical number system).
If the first character can not be converted to a number then it returns NaN.
Example
console.log(parseInt("55kg"));
console.log(parseInt(127.0234));
console.log(parseInt("a100"));7. toExponential Method In Javascript
The Number.toExponential() method converts numbers into exponential notation and returns them as a string.
This method accepts an optional argument which is an integer that specifies the number of digits after the decimal value.
Example
const num1 = 53455;
const num2 = 8362926;
console.log(num1.toExponential());
console.log(num2.toExponential(5));
console.log(Number.parseInt(3929).toExponential());8. toFixed Method In Javascript (round number)
The Number.toFixed() method in javascript formats the passed number using fixed-point notation. It is used to format a number with any specific number of digits.
Number.toFixed() method has a number argument that specifies the number of digits after decimal point
This method round of numbers as in maths.
Example
const num1 = 5.3455;
const num2 = 8.36499;
console.log(num1.toFixed());
console.log(num2.toFixed(2));
console.log(Number.parseFloat(3.929).toFixed(2));9. toLocaleString Method In Javascript (format number)
The Number.toLocaleString() method converts a Date object to a string using locale conventions.
It accepts an argument called locale used to get locale date for the country. Example en-AU (Australian English), en-IN (Indian English), bn-IN (Bangla India), etc.
Example
const today = new Date();
console.log(today.toLocaleString('en-AU'));
console.log(today.toLocaleString('en-IN'));
console.log(today.toLocaleString('bn-IN'));10. toPrecision Method In Javascript
The Number.toPrecision() method changes the number's precise value up to the passed number and returns the number as a string. Example: 125000's precision is 3.
This method accepts a number as an argument that defines precision.
Example
const num1 = 123456;
const num2 = 34.52353;
console.log(num1.toPrecision(3));
console.log(num2.toPrecision(4));11. toString Method In Javascript (number to string)
The Number.toString() method returns a string representing the number which invoked it.
This method accepts an optional argument that represents the base of the number system. If you pass 2 then the number will be converted to binary format and returned as a string. Its default value is 10.
Example
const num1 = 100;
const num2 = 8;
console.log(num1.toString(16));
console.log(num1.toString(8));
console.log(num2.toString(2));12. valueOf Method In Javascript
The Number.valueOf() method returns a primitive number for the specified object.
Example
const num1 = new Number(25);
console.log(num1.valueOf());
console.log(typeof num1.valueOf(), typeof num1);Conclusion
JavaScript Number object hold multiple properties and methods. The properties hold some important constants to be used in javascript while dealing with numbers. The methods are of different types static and instance methods.
